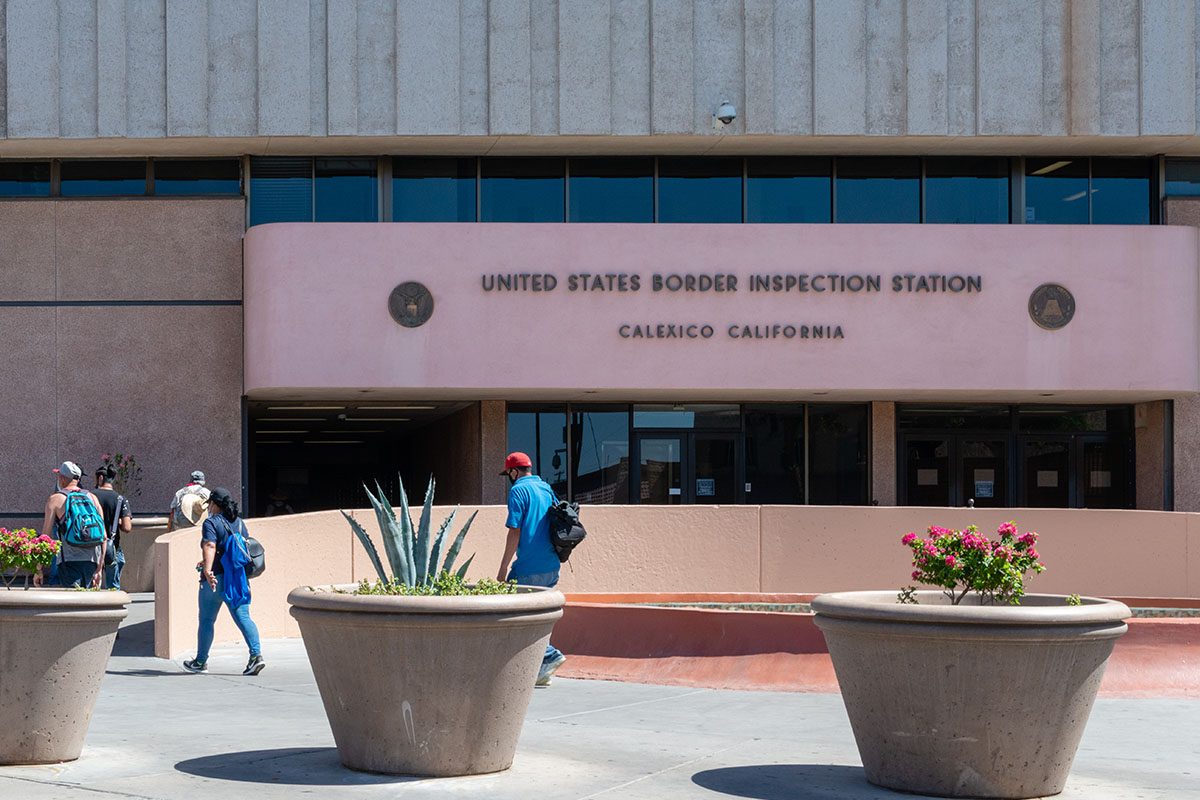
From El Centro Regional Medical Center, the largest hospital in California’s Imperial County, it takes just 30 minutes to drive to Mexicali, the capital of the Mexican state of Baja California. The international boundary that separates Mexicali from Imperial County is a bridge between nations. Every day, thousands of people cross that border for work or school. An estimated 275,000 US citizens and green card holders live in Baja California. El Centro Regional Medical Center has 60 employees who reside in Mexicali and commute across the border, CEO Adolphe Edward told Julie Small of KQED.

Now these inextricably linked places have become two of the most concerning COVID-19 hot spots in the US and Mexico. While Imperial County is one of California’s most sparsely populated counties, it has the state’s highest per capita infection rate — 836 per 100,000, according to the California Department of Public Health. This rate is more than four times greater than Los Angeles County’s, which is second-highest on that list. Imperial County has 4,800 confirmed positive cases and 64 deaths, and its southern neighbor Mexicali has 4,245 infections and 717 deaths.
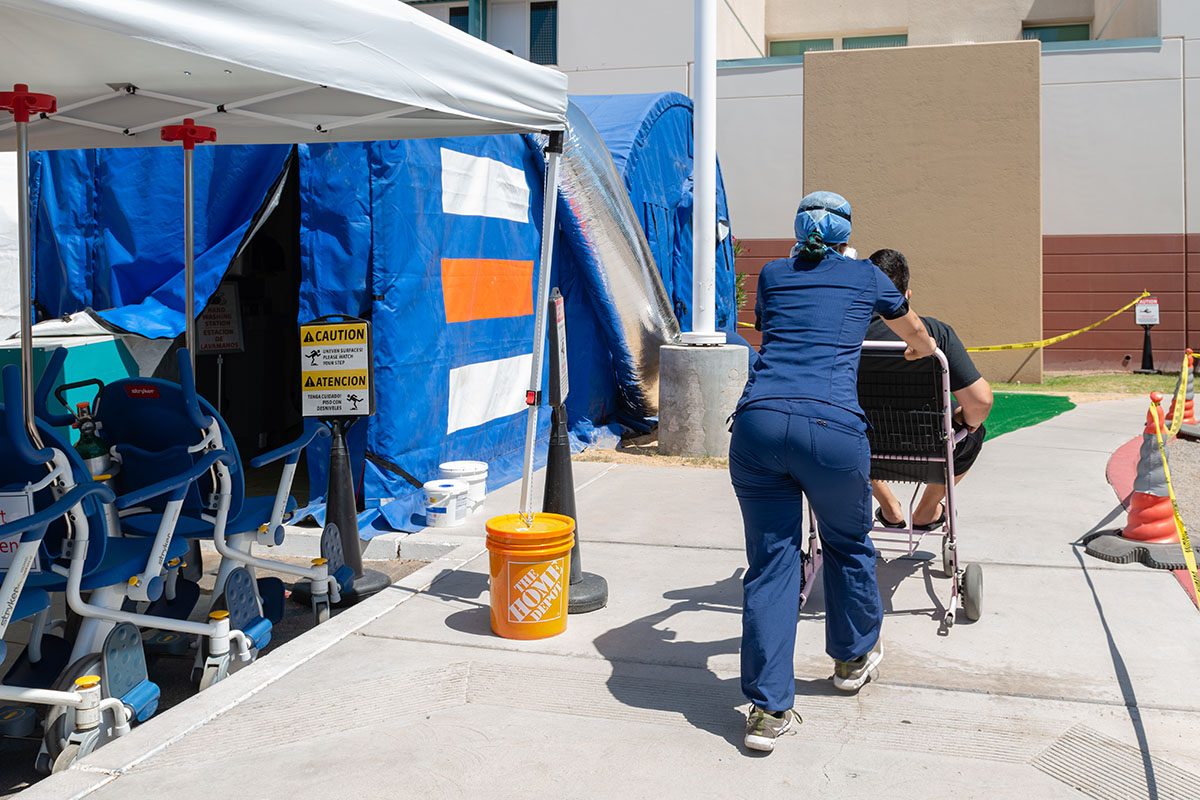
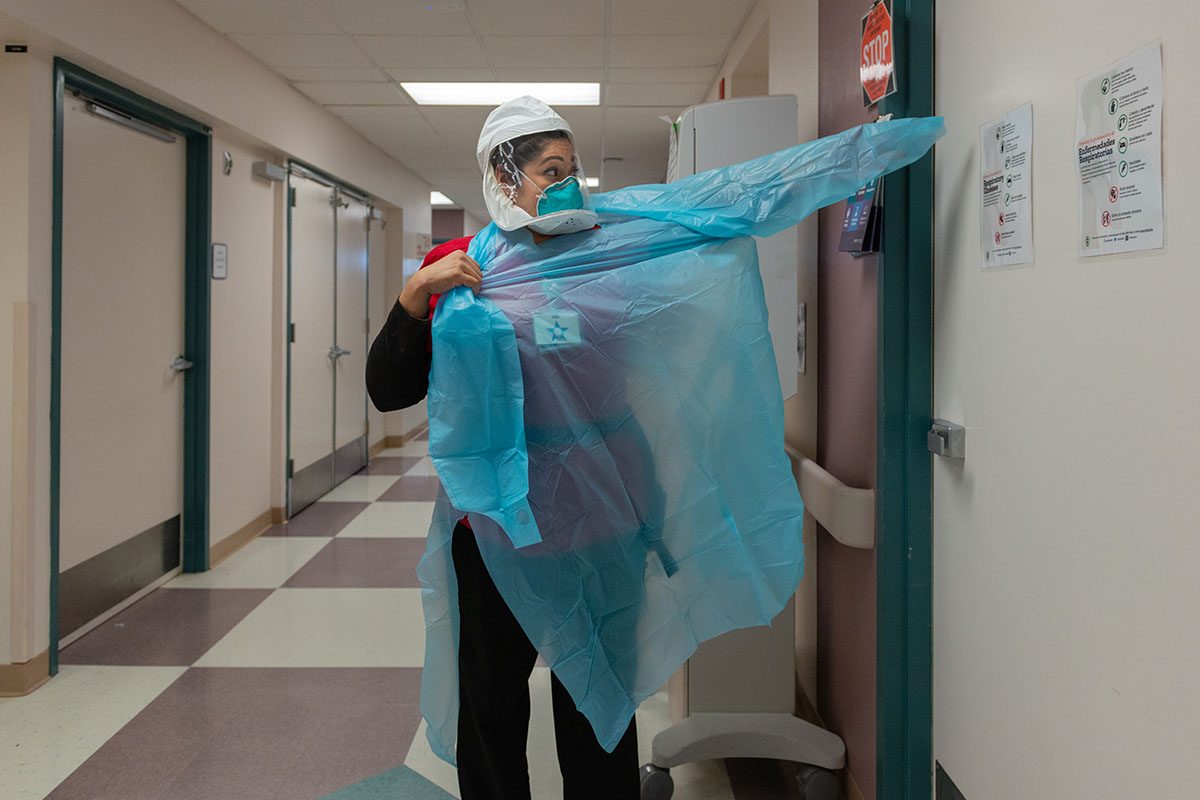
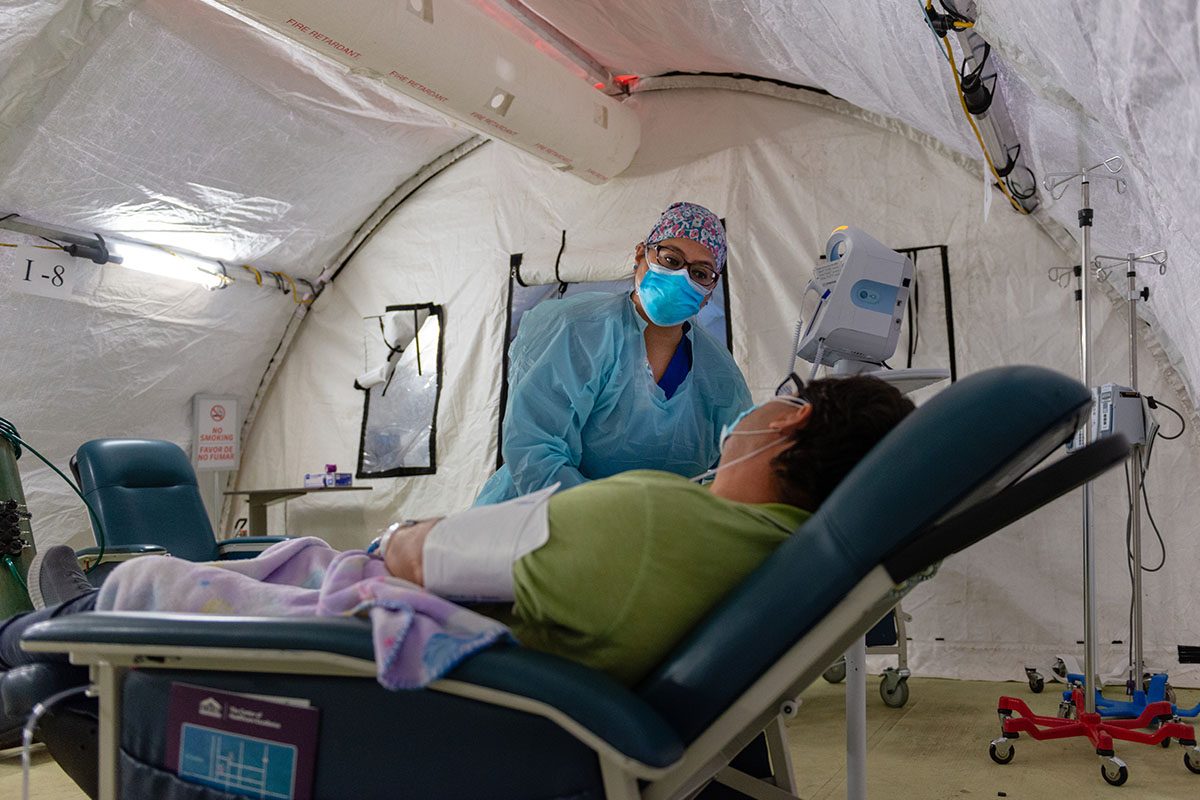
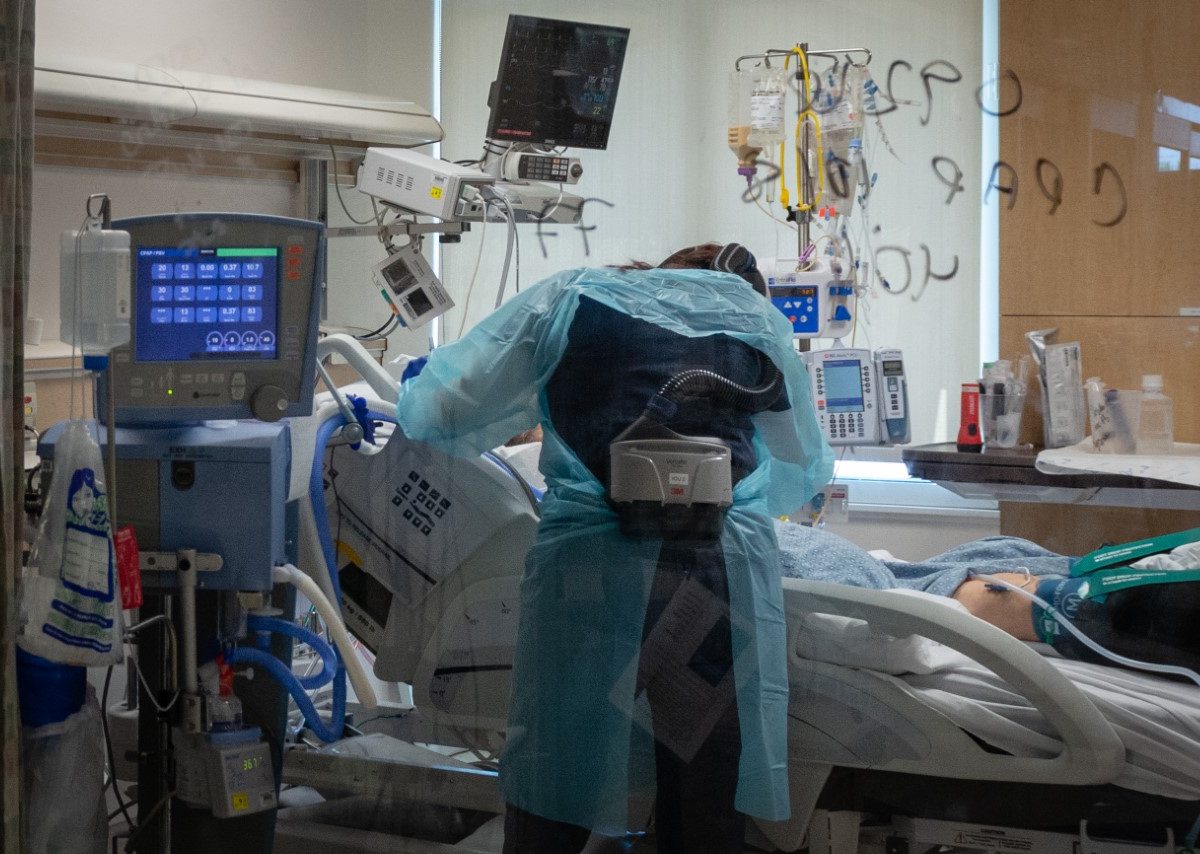
The COVID-19 crisis on the border is straining the local health care system. El Centro Regional Medical Center has 161 beds, including 20 in its intensive care unit (ICU). About half of all its inpatients have COVID-19, Gustavo Solis reported in the Los Angeles Times, and the facility no longer has any available ventilators.
When Mexicali’s hospitals reached capacity in late May, administrators alerted El Centro that they would be diverting American patients to the medical center. “They said, ‘Hey, our hospitals are full, you’re about to get the surge,’” Judy Cruz, director of El Centro’s emergency department, recounted to Rebecca Plevin in the Palm Springs Desert Sun.
By the first week of June, El Centro was so overburdened that “a patient was being transferred from the hospital in El Centro every two to three hours, compared to 17 in an entire month before the COVID-19 pandemic,” Miriam Jordan reported in the New York Times.
Border Hospitals Filled to Capacity
Since April, hospitals in neighboring San Diego and Riverside Counties have been accepting patient transfers to alleviate the caseload at the lone hospital in El Centro, but the health emergency has escalated and now those counties need relief. “We froze all transfers from Imperial County [on June 9] just to make sure that we have enough room if we do have more cases here in San Diego County,” Chris Van Gorder, CEO of Scripps Health, told Paul Sisson in the San Diego Union-Tribune. El Centro patients are now being airlifted as far as San Francisco and Sacramento.
According to the US Census Bureau, nearly 85% of Imperial County residents are Latino, and statewide, Latinos bear a disproportionate burden of COVID-19. The California Department of Public Health reports that Latinos make up 39% of California’s population but 57% of confirmed COVID-19 cases.
Nonessential travel between the US and Mexico has been restricted since March 21, with the measure recently extended until July 21. However, jobs in Southern California, such as in agricultural fields and packing houses, require regular movement between the two countries. “I’m always afraid that people are imagining this rush on the border,” Andrea Bowers, a spokesperson for the Imperial County Public Health Department, told Small. “It’s just folks living their everyday life.”
Working conditions at these jobs, some of which are considered essential because of their role in the food supply chain, may have contributed to the COVID-19 crisis on the border. Agricultural workers are rarely given adequate personal protective equipment and are unable to practice physical distancing. They also are exposed to air pollution, pesticides, heat, and more — long-term exposures that can cause the underlying health conditions that raise the risk of death for COVID-19 patients.
Comite Civico del Valle, a nonprofit focused on environmental health and civic engagement in Imperial Valley, set up 40 air pollution monitors throughout the county and found that levels of tiny, dangerous particulates violated federal limits, Solis reported.
“I can tell you there’s hypertension, there’s poor air pollution, there’s cancers, there’s asthma, there’s diabetes, there’s countless things people here are exposed to,” David Olmedo, an environmental health activist with Comite Civico del Valle, told Solis.
Fear of New Surges
With summer socializing in full swing, health experts worry that COVID-19 spikes will follow. Imperial County saw surges after Mother’s Day and Memorial Day, probably because of lapsed physical distancing and mask use at social events.
Latinos in California are adhering to recommended public health behaviors to slow the spread of the virus. CHCF’s recent COVID-19 tracking poll with Ipsos asked Californians about their compliance with recommended behaviors. Eighty-four percent of Californians, including 87% of Latinos, say they routinely wear a mask in public spaces all or most of the time. Seventy-two percent of Californians, including 73% of Latinos, say they avoid unnecessary trips out of the home most or all of the time, and 90% of Californians, including 91% of Latinos, say they stay at least six feet away from others in public spaces all or most of the time.
A Push to Reopen Anyway
Most counties in California have met the state’s readiness criteria for entering the “Expanded Stage 2” phase of reopening. Imperial County has not. In the past two weeks, more than 20% of all COVID-19 tests in the county came back positive, the Sacramento Bee reported. The state requires counties to have a seven-day testing positivity rate of no more than 8% to enter Expanded Stage 2.
Still, the Imperial County Board of Supervisors is pushing Governor Gavin Newsom for local control over its reopening timetable. The county has a high poverty rate — 24% compared with the statewide average of 13% — and “bills are stacking up,” Luis Pancarte, chairman of the board, said on a recent press call.
He worries that because neighboring areas like Riverside and San Diego have opened some businesses with physical distancing measures in place, Imperial County residents will travel to patronize restaurants and stores. This movement could increase transmission of the new coronavirus, just as reopening Imperial County too soon could as well.
More than 1,350 residents have signed a petition asking Newsom to ignore the Board of Supervisor’s request, Solis reported. The residents called on the supervisors to focus instead on getting the infection rate down and expanding economic relief for workers and businesses.
Cruz, who has been working around the clock to handle the county’s COVID-19 crisis, agrees with the petitioners. The surges after Mother’s Day and Memorial Day made her “really concerned about unlocking and letting people go back to normal,” she told Plevin. “It’s going to be just like those little gatherings that happened [on holidays], but on a bigger scale.”
Authors & Contributors